원본 : www.jkelec.co.kr/img/sensors/manual/mpu6050_gy521/mpu6050_gy521_manual.html
이 매뉴얼은 주식회사 제이케이이엠씨(JK EMC) 에 의해서 번역, 수정, 작성 되었고 소유권 또한
주 식회사 제이케이이엠씨(JK EMC)의 것입니다. 소유권자의 허가를 받지 않고 무단으로 수정, 삭제하거나 배포 할 수 없습니다.
MPU6050 3축 자이로,가속도 GY-521 3.3/5V 레귤레이터 내장형 센서 메뉴얼
* Update history
- 2016.8.3 : 프로세싱 코드 추가
- 2016.7.15 : 초기 Release
1. MPU6050 센서 소개
2. 아 두이노와 같이 사용하기
2.1 센서 회로도및 외곽 치수
2.2 아두이노 UNO R3 배선도
2.3 아두이노 스케치 코드
3. 프로세싱을 이용해서 3차원 그래픽 표시
3.1 프로세싱 설치 하기
3.2 아두이노 UNO R3 배선도
3.3 아두이노 스케치 코드
3.4 프로세싱 코드
1. MPU6050 센서 소개
MPU6050은 가속도와 자이로센서가 1개의 센서에 모두 포함하고 있는 6DOF(Degrees of Freedom) 센서이다. MPU6050은 I2C (Inter Integrated Circuit) 통신 프로토콜을 통해서 데이터를 추출 할 수 있다.
| 센서 사양 | Gyroscope(MPU6050) | Accelerometer(MPU6050) |
| Interface | I2C interface | I2C interface |
| Startup | 100 ms | 100 ms |
| Max range | ±2000 d/s | ±16G |
| Min range | ±250 d/s | ±2G |
| Resolution(Max) | 16.4 LSB/(degree/s) | 2048 LSB/(degree/s) |
| Resolution(Min) | 131 LSB/(degree/s) | 16384 LSB/(degree/s) |
| Update rate | 4 ~ 8000 hz | 4 ~ 1000 hz |
2. 아두이노와 같이 사용하기
2.1 센서 회로도및 외곽 치수
(1) MPU6050 센서 회로도
- MPU6050 PDF 회로도 다운로드
- MPU6050 데이터시트 다운로드(http://www.invensense.com)
- MPU6050 데이터시트 다운로드(http://www.jkelec.co.kr)
- MPU6050 DXF 캐드 파일 다운로드

(2) MPU6050 센서 외곽(mm단위) 치수

2.2 아두이노 UNO R3 배선도
(1) 아두이노 UNO R3와 연결해서 가속도, 자이로 센터 데이터 출력 하기
이번 예제에서는 인터럽트를 사용하지 않기 때문에 INT핀을 연결할 필요는 없다. 본 제품은 내부에 회로적으로 3.3V전원 레듈레이터와 I2C 레벨쉬프터를 내장하고 있어서 5.0V와 3.3V 에서 모두 사용이 가능 하다. STM32, 라즈베리파이 등과 같이 3.3V 전원을 사용하는 프로세서에서 사용할 경우에는 VCC 대신에 3.3V 핀을 통해서 전원을 바로 연결해 주면 된다.
- Fritzing 파일 다운로드

2.3 아두이노 스케치 코드
단순히 센서의 데이터를 시리얼 데이터로 출력하는 예제 이다.
(1) 아두이노 스케치 코드
- MPU6050 raw 데이터 표시 스캐치 파일 다운로드
|
MPU6050의 Slave Address는 기본적으로 0x68이고 본 제품에서도 AD0핀이 회로적으로 풀 다운 되어있다. 만약 MPU6050의 AD0핀을 풀업(VCC 3.3V 에 연결)을 시킨다면 Slave Address를 0x60로 수정 하여야 한다.
#define MPU6050_I2C_ADDRESS 0x68
MPU6050을 아두이노나 다른 마이크로 프로세서에서 동시에 2개를 사용해야 한다면 1개는 풀다운 그대로 사용을 하고 나머지 한개를 풀업 시켜서 Slave Address를 다르게 해서 사용을 하면 된다.
(2) 실행 결과
MPU6050과의 I2C 통신 상태를 검사하고 가속도, 자이로, 온도 값을 반복해서 보여준다.

본 메뉴얼의 아두이노 코드는 아래 https://github.com/jrowberg/i2cdevlib 의 내용을 참조하여 작성 하였다.
3. 프로세싱을 이용해서 3차원 그래픽 표시
3.1 프로세싱 설치 하기
아두이노를 이용해서 센서에서 데이터를 추출해서 시리얼 데이터로 출력을 해서 데이터 값을 확인을 쉽게 할 수 있었다. 그렇다면 텍스트 데이터가 아니라 조금더 시각적인 표현 방법이 없을까? 그것도 아주 쉽게..
프로세싱을 이용하면 아두이노 스케치 코드를 입력하듯이 아주 쉽게 시각적인 표현이 가능하다. 우선 프로세싱 개발 환경을 설치하는것부터 해보자.
(1) 프로세싱 설치
- 프로세싱 개발환경 설치 하기(새창)
(2) 3D 라이브러리 설치
- 이번 예제를 실행시키기 위해서는 toxiclibs 라이브러리가 필요하다.
- https://bitbucket.org/postspectacular/toxiclibs/downloads/ 에서 다운로드 받을수 있고 본 예제에서는 toxiclibs-complete-0020.zip 버전을 사용하였다.
- toxiclibs 파일 다운로드(www.jkelec.co.kr 에서도 다운로드 받을 수 있다.)
- 라이브러리 설치 위치는 프로세싱에서 "파일/환경 설정" 을 보면

"스케치 폴더 위치" 를 지정하는 항목이 있다.

"스케치 폴더 위치/libraries" 폴더에 다운로드 받은 toxiclibs-complete-0020.zip 압축 파일을 해제해서 넣어 놓으면 된다. 라이브러리를 새로 설치하고 나면 프로세싱 프로그램을 종료하고 다시 시작해야 적용이 완료 된다.

toxiclib 라이브러리가 모두 설치된 화면이다. 위 그림에서 json4processing 라이브러리는 본 예제를 실행 하는데는 필요하지 않다. 여기 까지 프로세싱 코드 실행을 위한 모든 준비가 되었다. 프로세싱코드는 MPUP6050 모듈에서 출력하는 데이터를 시리얼(RS232) 통신을 통해서 입력을 받아 데이터를 처리 하도록 되어 있다. 이제 아두이노와 MPU6050 모듈을 이용해서 프로세싱에서 처리 하기 위한 데이터 출력을 해보자.
3.2 아두이노 UNO R3 배선도
이전 예제 에서는 MPU6050의 INT 핀을 사용하지 않았는데 이번 예제에서는 아두이노에서 인터럽트를 사용하고 있기 때문에 INT핀을 아두이노의 D2핀에 연결을 해주었다. 나머지 배선도는 이전 예제와 동일하다.
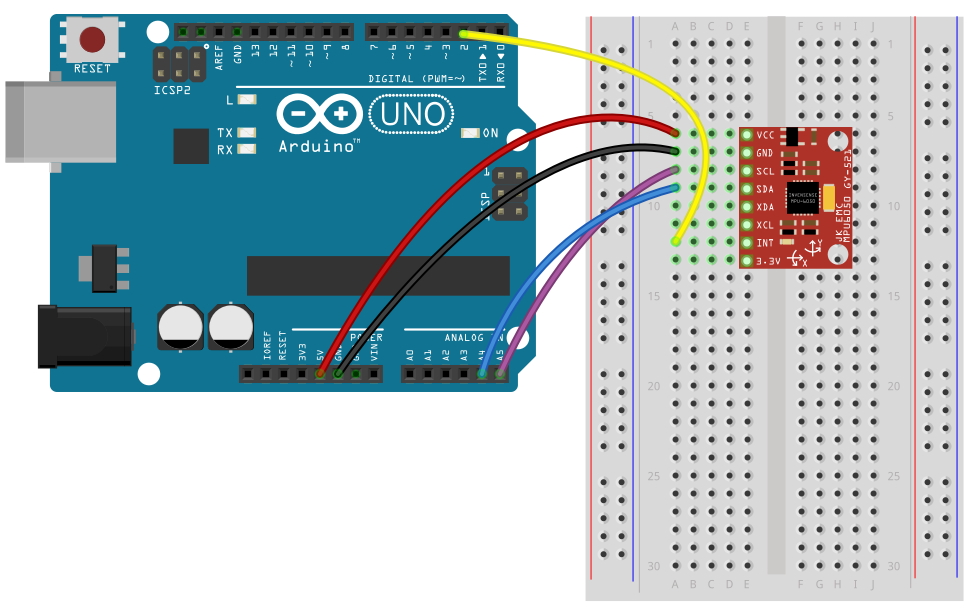
3.3 아두이노 스케치 코드
(1) 아두이노 프로세싱 코드
프로세싱 코드에서 한가지 주의 해야할 사항은 처리 속도를 빠르게 하기 위해서 시리통 통신의 속도를 115200bps 로 설정을 하였다. 그렇기 때문에 아두이노의 시리얼 모니터창에서도 동일한 통신속도를 맞추어 주어야 한다.
- MPU6050 아두이노, 프로세싱 스캐치 파일 다운로드
|
(2) 실행 결과

아두이노 시리얼 모니터창에서 반드시 보드레이트(Baudate)를 115200 으로 수정 해야 한다. 그렇지 않으면 시리얼 모니터 창에 아무런 데이터가 표시되지 않거나 잘못된 데이터가 표시될 것이다. 프로세싱 데이터를 처리하기 위한 데이터 이므로 데이터를 바로 판독하기는 어렵다. 데이터가 올바르게 표시되는것을 확인 하였다면 프로세싱에서 동일한 시리얼포트를 사용해야 하기 때문에 아두이노 시리얼 모니텅 창을 닫도록 하자.
3.4 프로세싱 코드
프로세싱 코드에서 한가지 주의 해야할 사항은 시리얼 포트를 각자의 환경에 맞추어서 수정을 해주어야 한다는 것이다.
아래 프로세싱 코드에서 "[0]" 의 0이라는 숫자는 장치관리자에서 COM포트의 번호가 아니라 포트의 순서라는것에 주의 해야 한다.

위의 장치관리자 화면에서 예를 든다면 다음과 같다.
String portName = Serial.list()[0]; // --> COM31String portName = Serial.list()[1]; // --> COM5
프로세싱 코드를 실행할때 테스트하는 PC의 COM 포트 상태에 따라서 "Serial.list()[0]" 의 숫자를 바꾸어 주어야 한다.
(1) 프로세싱 코드
|
(2) 실행 결과
본 메뉴얼의 프로세싱 코드는 아래 URL의 내용을 참조하여 작성 하였다.
http://www.instructables.com/id/MPU6050-Arduino-6-Axis-Accelerometer-Gyro-GY-521-B/?ALLSTEPS
* 다른 센서들의 아두이노와 프로세싱 메뉴얼 보기
(1) MPU6050 GY-521 센서 아두이노, 프로세싱 메뉴얼(새창)
(2) MPU9250 GY-9250 센서 아두이노, 프로세싱 메뉴얼(새창)
(3) L3G4200D GY-50 센서 아두이노, 프로세싱 메뉴얼(새창)
(4) HMC5883L GY-271 센서 아두이노, 프로세싱 메뉴얼(새창)
(5) BMP180 GY-68 센서 아두이노, 프로세싱 메뉴얼(새창)
(6) ADXL345 GY-80 센서 아두이노, 프로세싱 메뉴얼(새창)
(7) ADXL335 GY-61 센서 아두이노, 프로세싱 메뉴얼(새창)
